Site-to-Site vs. Client-to-Site VPNs: Key Differences and Use Cases
- May 4, 2025
- 11 minutes Read
- Security & Privacy
Exactly what brings us to the comparison of Site-to-site vs. Client-to-site VPN?
Imagine two remote offices in different locations need to share data securely, or you’re a remote worker who needs secure access to company resources.
What would be the best way to resolve this? You require a secure VPN solution.
Site-to-site VPNs are designed to connect entire networks, such as offices or data centers. They create a secure tunnel between the two networks, allowing them to communicate as if they were physically connected.
On the other hand, Client-to-Site VPNs are ideal for individual users to connect securely to a remote network. For example, a remote employee can use a Client-to-Site VPN to access their company’s network and resources from home.
This blog will explore the key differences, use cases, advantages, and more about these two types of Virtual Private Networks. Let’s start.
Table of contents
What is a Site-to-Site VPN?
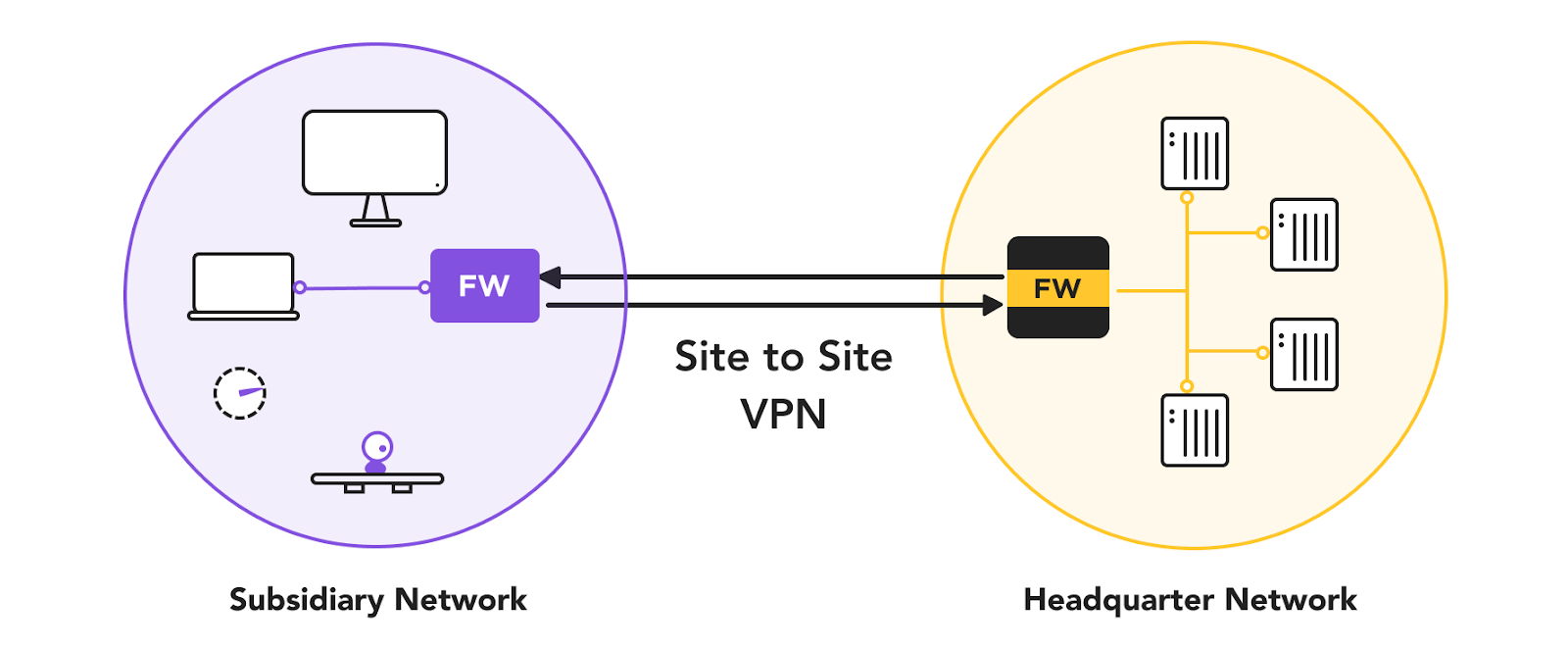
Image Source: Firewalla
Site-to-site VPNs connect two or more private networks, allowing them to communicate as if they were on the same local area network (LAN). Due to their characteristics, they are also known as network-to-network VPNs.
Site-to-site VPNs establish a secure and encrypted tunnel between two locations, carrying data from one place to another. Each site has a VPN gateway that encrypts outgoing data for internet transmission.
This encrypted tunnel ensures that interceptors cannot read intercepted data without authorization. When the data reaches the destination gateway, it is decrypted and given to the appropriate user on the local area network.
Security and Encryption
Site-to-site VPNs usually secure inter-site connections. They utilize IPsec protocols to create encrypted tunnels between multiple sites, securing all traffic.
Performance
Site-to-site VPNs typically offer higher performance, connecting entire networks rather than individual users. Performance can be optimized with MPLS configurations, allowing for lower latency and better bandwidth management.
Scalability
Site-to-site VPNs are highly scalable. New sites can be added by installing a VPN gateway at each location without configuring individual clients.
Use Cases
Site-to-site VPNs are used for security, scalability, and centralized control.
In organizations with branch offices, employees can securely access files, databases, and applications through secure network connections using site-to-site VPNs. This helps businesses and organizations to keep their data safe from unauthorized access.
It also enables the efficient sharing of sensitive information across various locations without exposing it to potential threats to the public network.
Advantages of Site-to-site VPNs
1. Data Protection and Confidentiality: Site-to-site VPNs protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. It ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the data during transmission.
2. Scalability and Infrastructure Expansion: It allows businesses to expand their operations by simplifying and updating the existing infrastructure relatively easily, making it a scalable solution.
3. Centralized Network Management: IT administrators can manage network security policies and configurations from a central point. This simplifies system monitoring and enhances security measures across all connected locations. Choose this VPN if you need a business VPN solution.
Disadvantages of Site-to-Site VPNs
1. High Setup Costs: Deploying Site-to-Site VPNs often requires expensive hardware like routers, firewalls, and dedicated VPN appliances. This can be a significant upfront investment for small or mid-sized businesses.
2. Complex Configuration: Setting up and maintaining Site-to-Site VPNs requires experienced network administrators. The complexity increases with the number of branches or connected networks.
3. Limited Flexibility for Small Scale Users: Site-to-site VPNs are designed for static environments. They are not ideal for remote or mobile users who need to connect from various locations.
4. Scalability Challenges for Rapid Growth: While scalable for large infrastructures, sudden expansion or dynamic remote access needs can require redesigning the VPN architecture.
5. Network Wide Exposure: Once connected, users from either side can access the entire network. The whole network can be at risk if any connected system is compromised.
What is a Client-to-Site VPN?
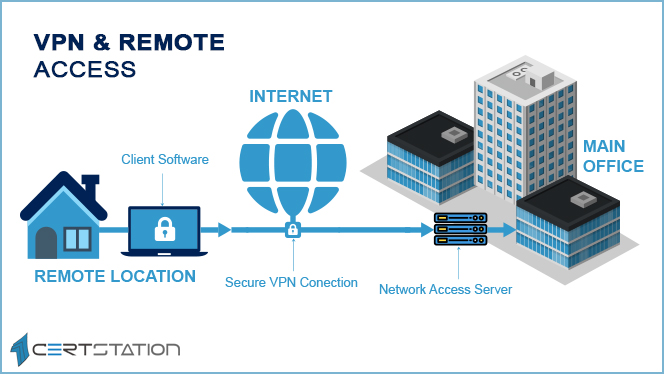
Image Source: Cert Station
Client-to-site VPN allows individual users to securely connect their devices to a corporate network over the internet. This is particularly useful for remote employees who need access to company resources outside the office.
Because of this, they’re also known as remote-access VPNs.
It usually operates on a simple client-based model: users install VPN client software on their preferred devices, such as laptops or smartphones. When the user wants to connect, this client software initiates the user’s VPN connection.
It authenticates the user and establishes a secure connection to the corporate network. Once connected, all data transmitted between the user’s device and the corporate network is encrypted. This makes it an ideal VPN for remote employees.
Security and Encryption
Client-to-site VPN encrypts data between individual clients and corporate networks using SSL or IPsec protocols. Each connection is authenticated, ensuring remote users have secure access to corporate resources from anywhere in the world.
Performance
It is generally suitable for individual users, but multiple simultaneous connections may experience latency. Performance can vary based on other critical factors, such as the users’ internet connection condition and the load on the VPN server.
Scalability
Client-to-site VPNs offer limited scalability. Adding more users requires additional client configuration and can lead to management challenges as user numbers increase.
Use cases
Client-to-site VPNs are ideal for remote users accessing a corporate network. Employees working from home or other remote locations can securely connect to their company’s network to access necessary information.
Business travelers can use client-to-site VPNs to connect to their corporate networks from various locations, such as hotels or airports.
Advantages of Client-to-site VPN
1. Flexible to Use: Client-to-site VPN provides flexibility, easy access, and convenience for users. This VPN lets users connect virtually anywhere via the internet, providing flexibility in work locations.
2. Easy to Configure: The setup allows users to access corporate resources without needing complex configurations for each device.
3. Highly Secured: Employees can work securely from their devices without compromising sensitive company data, which is convenient for users and IT departments.
Disadvantages of Client-to-Site VPNs
1. Performance Variability: The connection quality depends on the user’s internet speed and device performance. Poor bandwidth or outdated hardware can affect productivity.
2. High Maintenance for Large User Bases: Each user requires individual setup and ongoing support. Managing hundreds of remote users can strain IT teams.
3. Device-Level Security Risks: Security depends heavily on each user’s device. If a user’s laptop or phone is compromised, it can serve as a gateway for attacks.
4. Manual User Authentication: Users must log in manually each time they connect, which can lead to usability issues or delays, especially in high-frequency access scenarios.
5. License and Subscription Costs: Although cheaper upfront, costs can increase with the number of users due to licensing fees, subscriptions, or VPN client software requirements.
Site-to-Site vs. Client-to-Site VPNs: Key Differences
Each VPN type serves a different purpose and user base. Understanding their main differences helps businesses and individuals choose the right solution. Here’s a detailed comparison between these two VPNs:
Architecture Differences
- In a Site-to-Site setup, the connection is established between two or more networks. No user-specific configuration is required. Encryption and tunneling protocols handle data transfer between the networks.
- For Client-to-Site VPNs, each user installs software on their device. The software creates an encrypted tunnel to the remote network. Authentication methods like passwords or certificates ensure secure access.
Security Structure
- Site-to-Site VPNs rely on robust encryption standards like AES-256. Firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) often complement the setup. These measures protect sensitive data during transmission.
- Client-to-Site VPNs focus on securing individual connections. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is frequently used to verify user identity. Regular updates to client software ensure protection against vulnerabilities.
Scalability and Maintenance
- Site-to-Site VPNs scale better for organizations with multiple branches. Once configured, adding users doesn’t require new setups.
- Client-to-Site VPNs need individual configuration per user. Managing large numbers of remote users can become time-consuming.
Performance and Bandwidth
- Site-to-Site VPNs generally offer higher performance. The connection runs through dedicated network hardware.
- Client-to-Site VPNs can be affected by the user’s internet speed and device capability. Performance may vary from user to user.
Cost and Resources
- Initial setup costs for Site-to-Site VPNs can be high. Hardware like routers and firewalls, along with IT expertise, adds to expenses. However, long-term operational costs are lower for large-scale deployments.
- Client-to-Site VPNs have lower upfront costs. Individual licenses or subscriptions are affordable. Ongoing expenses may increase as more users join the network.
Setup and Configuration
- Site-to-Site VPNs are configured on routers or firewalls. The connection is automatic once set up. No manual login is needed from users.
- Client-to-Site VPNs require software to be installed on each device. Users must log in to establish the connection. It’s user-specific, not network-wide.
Network Access Control
- In a Site-to-Site VPN, users gain access to the entire connected network. It’s ideal for full office integration.
- Client-to-Site VPNs give access only to authorized users. Each login is monitored. Admins can assign specific access rights based on roles.
Here’s a quick comparison table between site-to-site vs client-to-site VPN:
| Criteria | Site-to-Site VPN | Client-to-Site VPN |
| Architecture | Connects entire networks without user-specific setup; uses encryption for tunneling | Each user installs software to create a secure tunnel; authentication is required |
| Setup & Configuration | Configured on routers or firewalls; auto-connects once set up | Requires client software on each device; users must log in manually |
| Network Access Control | Full network access for all devices on connected networks | Access is granted per user; admins manage individual permissions |
| Security Structure | Secured at the network level; less exposed to endpoint threats | Depends on endpoint security; compromised devices pose higher risk |
| Security Features | Utilizes AES-256 encryption, firewalls, and IDS for secure data transfer | Uses MFA and secure authentication; regular software updates for client protection |
| Scalability | Ideal for large organizations and multiple branches | Scales easily for small teams; suitable for flexible or mobile workforces |
| Maintenance | Easier to manage over time; user additions don’t require new configurations. | Requires individual user setup and ongoing maintenance |
| Performance | Offers stable and high-speed connections via dedicated hardware | Performance varies with device specs and internet quality |
| Bandwidth Usage | Optimized for high-volume inter-network traffic | May experience slowdowns during peak or multi-user access |
| Cost & Resources | High initial investment in hardware and IT resources; cost-effective long-term | Lower upfront costs; expenses grow as user base expands |
When to Choose Site-to-Site VPN?
It is ideal for businesses with multiple locations regarding interoffice communication control and data protection.
Suppose your organization has multiple offices or branches that need to communicate regularly. It allows all locations to communicate securely without client software.
Also, a site-to-site VPN ensures secure data transmission if your business deals with sensitive data (e.g., user credentials, financial documents, etc.).
Additionally, if your IT department wants to streamline network management, site-to-site VPNs offer centralized control over security policies and configurations across sites.
Site-to-site VPNs are highly scalable and can easily accommodate this growth without extensive reconfiguration. This is particularly beneficial if your business or organization plans to expand to different locations by adding new branches.
When to Choose Client-to-Site VPN?
This type of VPN is ideal for businesses with remote employees or individuals who need secure access to company resources from anywhere in the world. It’s also convenient for workers on the go and in hybrid working environments.
If employees work from home or travel frequently, a client-to-site VPN lets them connect securely to the corporate network from various locations.
Also, smaller businesses with fewer employees requiring access to the company LAN may find client-to-site VPNs more cost-effective than Site-to-site VPNs.
Businesses or organizations that need flexibility in allowing different users to connect from various devices or locations can use Client-to-site VPNs.
Final Words
We hope you have a clear idea of Site-to-Site vs. Client-to-Site VPNs.
Choose a Site-to-Site VPN for organizations with multiple fixed locations requiring secure interoffice communication and centralized management.
Opt for a Client-to-Site VPN when individual remote access is needed, particularly for smaller organizations or those with remote users or employees.
Meanwhile, if you’re curious about the difference between Layer 2 and Layer 3 MPLS VPN, head to our cybersecurity blog to learn more.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use both types of VPNs simultaneously?
Yes, using both Site-to-site and Client-to-site VPNs simultaneously within an organization is possible. The hybrid setup provides comprehensive coverage, flexibility, optimized resource sharing, and secure communication.
What’s the best VPN type for a small business?
The best VPN type for a small business typically depends on its specific needs. Client-to-site VPNs are ideal for remote employees, whereas site-to-site VPNs are more suitable for medium to large businesses with multiple physical offices.
Are Site-to-Site VPNs more secure than Client-to-Site?
Yes, Site-to-Site VPNs are generally more secure because they operate at the network level, reducing endpoint vulnerabilities. In contrast, Client-to-Site VPNs rely on individual device security, which increases the risk if user devices are compromised.
What are the typical costs associated with each type of VPN?
Site-to-Site VPNs typically involve higher upfront costs, including routers, firewalls, and IT setup. However, they offer lower long-term costs for large networks. Client-to-Site VPNs have lower initial costs, usually limited to software licenses, but expenses grow as more users join and require support.
![Ultimate White Label VPN Business Guide 2026 [Cost & ROI]](https://symlexvpn.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Ultimate-White-Label-VPN-Business-Guide-2025-Cost-ROI_2-376x114.webp)