Password VS Passphrase: Which One to Use?
- February 7, 2024
- 8 minutes Read
- Security & Privacy
Passphrases are more secure than Passwords. The main difference between them is that passphrases combine random words to make phrases, whereas passwords are mixed numbers, letters, and symbols.
This blog will delve into a deeper discussion on Password vs Passphrase.
Table of contents
Password vs Passphrase: Comparison
Here’s a quick comparison between the factors of password and passphrase.
| Feature | Password | Passphrase |
| Length | Typically 8-12 characters | Usually longer, 15+ characters |
| Complexity | Requires a mix of different types of characters | Can just use words; less complexity is needed |
| Strength | Harder to crack with length/complexity | Strength through the longer length |
| Memorability | Harder to remember complex strings of characters | Easier to remember words and phrases |
| Convenience | It is faster to type short passwords | Length makes passphrases slower to enter |
| Security | More vulnerable to brute force attacks | Longer length increases security |
| Usage | Widely used and supported | Less universal support and usage |
| Customization | Greater flexibility and options for complexity | It is more limited since it focuses on words |
| User Habits | Passwords ingrained in most users | Passphrases less common and understood |
Now, let’s explore the differences, pros and cons, and use cases of passwords and passphrases in detail.

What is a Password?
Passwords are the combination of numbers, letters/alphabets, and symbols to gain access to a computer, network, account, or basically anything that is protected online.
Passwords can be 8-12 characters long and mix uppercase and lowercase letter symbols to make it more complex and secure.
Why Do You Need a Password?
Passwords help you to prevent unauthorized access to your digital asset. Only you can access the files, network, or computer with your unique password.
However, passwords are easier to crack with Bruteforce attacks and can be easily compromised. That’s why mixing uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols is recommended to make it longer and more complex.
Also, avoid using common words, names, birthdates, or phone numbers, which can easily be guessed and cracked. Furthermore, using the same password in multiple places is also not recommended.
Use a 2-factor authentication or biometric login along with the password. With a two-factor authentication enabled, nobody can access your account or files even if they know the password.
Characteristics of a Strong Password
- 8-12 Characters long (the longer, the better)
- Mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.(ex- bazKxl51pdlbSZV )
- No personal information like first name, last name, birth date, or a simple pattern like 123456 exists.
Why Do You Need a Password?
You need a password mainly for security reasons, but there are other key reasons why a password is crucial for your digital assets.
- Authentication: Passwords are one of the most important ways to protect and verify your identity online. Your unique password proves that you are trying to access your account.
- Security: Secure passwords prevent unauthorized access to your data, files, online accounts, and banking. Weak passwords are vulnerable to hacking and cracking by Bruteforce attacks.
- Privacy: Password is the key to accessing your private files and information across many sites and services. Thus, passwords help you to protect your privacy.
- Accountability: Logging into an account with your unique credentials leaves an audit trail showing that you accessed the account, which provides accountability.
For convenience and security, you can use Password Managers to remember and securely store your passwords.
The Pros & Cons of Passwords
Here are the potential pros and cons of passwords.
Pros
- Passwords are universally supported
- Passwords don’t need any extra hardware support
- Passwords are easy to remember
- Password can be of any length
Cons
- Passwords are vulnerable to Brute force attacks
- Passwords can be stolen through Phishing attacks
- Passwords are commonly re-used
- Passwords are vulnerable to social engineering
| Bad Password Pattern | Strength | Crackable? | Estimated Time for Cracking |
| Easy to type the spatial word. (example: qwert, 123456, pppppp, 98765 ) | Very weak | Yes | 18 milliseconds |
| Simple/common/easy to guess words. (Example: iamalex) | Very weak | Yes | 1 second |
| Short letters, numbers, and symbol combinations. (AlexAdams@1990) | Weak | Yes | 20 minutes |
| Family name, own name, birth date, pet’s name. (example: 15 Jan 1990) | Very weak | Yes | 2 days |
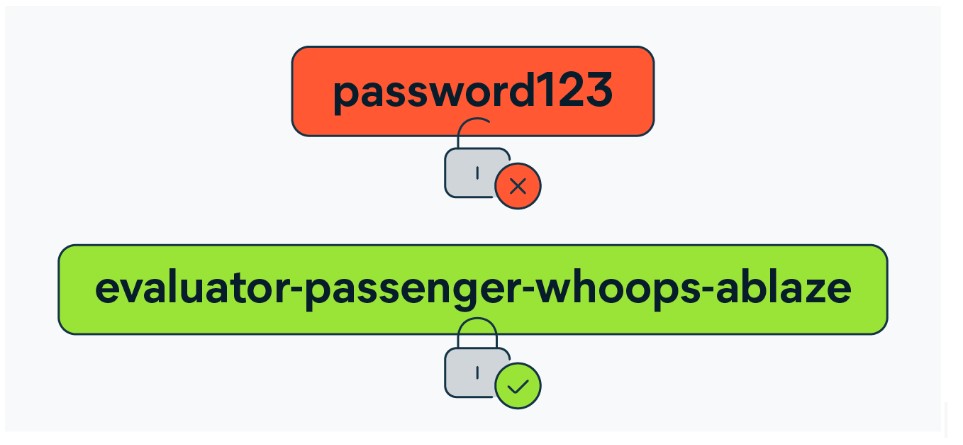
What is a Passphrase?
The passphrase is more secure than a password that contains random, unrelated words to make unique phrases. It can be of any length, but the longer, the better.
Passphrases can be more than 14 characters long. The basic idea behind passphrase is to make complex phrases out of completely unrelated word combinations to make them immune to Brute force or any other hacking attacks.
For example, guitar horse battery mechanic is a simple four-word passphrase with around 108,199,957 decillions or 1.08 x 10^41 possible combinations.
That means it would take around 25 years and more than 2 billion attempts per second to crack the passphrase. Isn’t it crazy? It explains how strong a passphrase can be.
If someone wants to crack your passphrase it will end up like the above picture. 😂
Characteristics of a Strong Passphrase:
- Random combinations of unrelated words.
- Typically longer than 15 characters. (the longer, the better)
- They don’t need to make sense or be grammatically correct.
- Passphrases are complex, and you don’t have to remember them.
- Automatically stored with biometric or device credentials.
Compared to passwords, here’s a secure passphrase pattern:
| Passphrase pattern | Strength | Crackable? | Estimated Time for Cracking |
| Four or five randomly chosen unrelated word combinations. Bullion Fame cheese defog() | Super duper strong | Technically not possible | 2,553 centuries |
Why do you need a Passphrase?
Passphrases are a better solution than passwords for your email account, social media account, cloud storage, and any other digital platform needing more security.
You should use passphrases for some major accounts/platforms and a password manager for the rest of your accounts.
The longer the passphrase, the better. Avoid using common and easy-to-guess passphrases like:
- I love coffee
- this is my birthday today
- my dog is a mixed breed
The Pros & Cons of Passphrase
Here are some possible pros and cons of using passphrases over passwords.
Pros
- Increased security due to length/complexity.
- Not knowledge-based. (don’t have to memorize)
- It can be up to 100 characters for stronger security.
Cons
- Vulnerable if common words/phrases are used.
- It can be compromised if carelessly stored.
How to Create a Strong Passphrase?
There are multiple easy ways to create a strong passphrase.
- Use online tools: You can easily generate strong passphrases using online tools. There are many tools available; find the one that suits you best.
- Use password managers: Use secure passwords to store and save your passphrase securely and use it whenever needed.
- Backup to the cloud: Save the passphrase to any secure cloud storage to avoid getting stolen or compromised.
- Use more than four words: Choose passphrases consisting of at least four or five words for maximum security.
3 Reasons to Use Passphrase Over Password
Here are the three major reasons to use a passphrase over a password.
Reason 1: More Secure Than Passwords
Passphrases are much longer than traditional passwords, with at least 4 or more random words. This significantly increases strength against brute force attacks. The length creates more combinations, which may take thousands of years to crack.
Reason 2: Comparatively Easier to Remember
Passphrases are easy to remember if it’s a four or five word combination. However, it’s possible to remember different passphrases for different accounts. So, keep the passphrases secure (zero-knowledge cloud storage).
Reason 3: Newer Encryption Technology
The passphrase is newer, more advanced, and more secure when integrated with hardware like biometric or device encryption. Google and Microsoft have recently encouraged users to use passphrases instead of passwords.
Why Passphrase or Password May Not Be Enough?
Even though you use a strong password or unbreakable passphrase to prevent a Bruteforce attack, it is still vulnerable to other cyber attacks. Your password or passphrase can be compromised if your connection is insecure.
Hackers are able to steal passwords easily with Phishing attacks through multiple ways like sending you spam emails, redirecting you to fake websites, or you end up downloading malwares on your device. Anything is possible!
A secure and trustworthy VPN service is recommended to prevent this. Passwords and passphrases protect your device’s online accounts, whereas a VPN keeps the connection encrypted and hidden from hackers or snoopers.
Final Words
Have a clear understanding of the detailed discussion on Passphrase vs Passwords. Both are used for security purposes and have advantages and disadvantages over one another. In general, Passphrases are a more secure and better solution than passwords due to their length, complexity, and ease of use.
![Ultimate White Label VPN Business Guide 2026 [Cost & ROI]](https://symlexvpn.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Ultimate-White-Label-VPN-Business-Guide-2025-Cost-ROI_2-376x114.webp)