
Does a VPN Prevent DDoS Attacks? The Truth You Need to Know
- March 17, 2025
- 9 minutes Read
- VPN Service
Facing continuous DDoS attacks that threaten your online presence? You’re not alone! Cyber threats are escalating in recent years, leaving businesses and individuals scrambling for protection. A VPN might be your first line of defense, but does a VPN prevent DDoS attacks?
Yes, a DDoS protected VPN can help prevent DDoS attacks to some extent by hiding your IP address and encrypting your traffic. When your IP address is hidden, it becomes difficult for attackers to locate your network, making it harder for them to target you. Additionally, a VPN can encrypt web traffic, creating a tunnel between your computer and the network you’re using, therefore hiding activity from your ISP.
Following part of this article, we’ll break down how VPNs work against DDoS threats, their limitations, and why choosing the right provider matters. Ready to safeguard your data and privacy? Lets discover the truth about VPNs and DDoS protection.
Table of contents
Does a VPN Prevent DDoS Attacks?
Source: https://bunny.net/
Yes, a VPN can help prevent DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service) attacks by masking your real IP address. Attackers often use your IP to flood your network with excessive traffic, causing slowdowns or disruptions of your network device.
A VPN routes your connection through secure servers, hiding your actual IP and making it harder for attackers to target your original IP directly.
Additionally, a good premium VPNs offer DDoS protection by detecting and filtering malicious traffic before it reaches your device. Some VPNs even have dedicated anti-DDoS servers designed to withstand high-traffic attacks.
However, while a VPN adds a layer of security, it is not a foolproof solution. If an attacker already has your IP or if your VPN internet provider suffers an attack, you may still experience network disruptions. For a comprehensive protection use combination of VPN with firewall rules, strong network security, and DDoS mitigation services.
How a VPN Prevents DDoS Attacks? (Step-by-Step Breakdown)
A VPN can help mitigate DDoS attacks by masking your IP address and encrypting your internet traffic. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a VPN can prevent or reduce the impact of DDoS attacks:
Step 1: Hides Your Real IP Address
When you connect to a VPN, your IP address is replaced with the IP address of the VPN server. DDoS attacks target a specific IP address. If attackers don’t know your real IP, they can’t directly target your device or network.
Step 2: Encrypts Your Traffic
A VPN encrypts all data transmitted between your device and the VPN server. While encryption doesn’t directly stop DDoS attacks, it makes it harder for attackers to intercept and analyze your traffic, reducing the risk of targeted attacks.
Step 3: Routes Traffic Through VPN Servers
Your internet traffic is routed through the VPN server, which acts as a protection layer between your device and the internet. If a DDoS attack targets the VPN server’s IP address, the VPN provider’s infrastructure is designed to handle large volumes of traffic, often mitigating the attack before it reaches you.
Step 4: Provides Access to DDoS-Protected Servers
Many premium VPN providers offer servers with built-in DDoS protection. These servers are equipped to absorb and filter out malicious traffic, ensuring your connection remains stable even during an attack.
Step 5: Allows Quick IP Address Changes
If a DDoS attack targets the VPN server’s IP address, you can quickly switch to a different server with a new IP address. This makes it difficult for attackers to continue an attack, as the target IP address keeps changing.
Step 6: Adds an Extra Layer of Anonymity
A VPN masks your online activities and makes it harder for attackers to identify you as a target. By reducing your visibility, a VPN lowers the chances of being targeted by DDoS attacks in the first place.
Limitations of a VPN Against DDoS Attacks
While a VPN provides some protection against DDoS attacks by masking your IP address, it is not a complete solution. Understanding its limitations can help you look for a more robust defense.
Does Not Prevent Pre-Existing IP Exposure
If an attacker already knows your real IP address before you connect to a VPN, they can still target your network if you are not using a VPN. It can only hide your IP while it’s active, so any previous leaks leave you vulnerable to attackers.
Not All VPNs Offer DDoS Protection
Many VPNs provide anonymity but lack specialized DDoS protection. Standard VPN servers can still be overloaded if attacked directly, making it crucial to choose a provider with high-capacity, anti-DDoS infrastructure.
Latency and Speed Issues
VPNs add an extra layer of encryption and reroutes traffic through remote servers. While this enhances security, it can introduce latency, which may affect gaming, streaming, or other real-time applications. If a VPN server itself experiences high traffic, your network performance will suffer.
Cannot Protect Against Layer 7 DDoS Attacks
DDoS attacks operate on different layers of the internet. A VPN effectively shields against network-layer (Layer 3 and 4) attacks that target IP addresses. However, it does not stop application-layer (Layer 7) attacks, which overload websites or online services by exploiting software vulnerabilities.
Potential VPN Server Targeting
If an attacker launches a DDoS attack against the VPN server you are connected to, your connection might slow down or become unstable. While some VPN providers use countermeasures, smaller providers may struggle to handle such attacks.
Limited Effectiveness for Large-Scale DDoS Attacks
Powerful DDoS attacks can send massive amounts of traffic, sometimes exceeding the capacity of VPN services. In extreme cases, even VPN-protected users may experience disruptions if the attack is powerful enough.
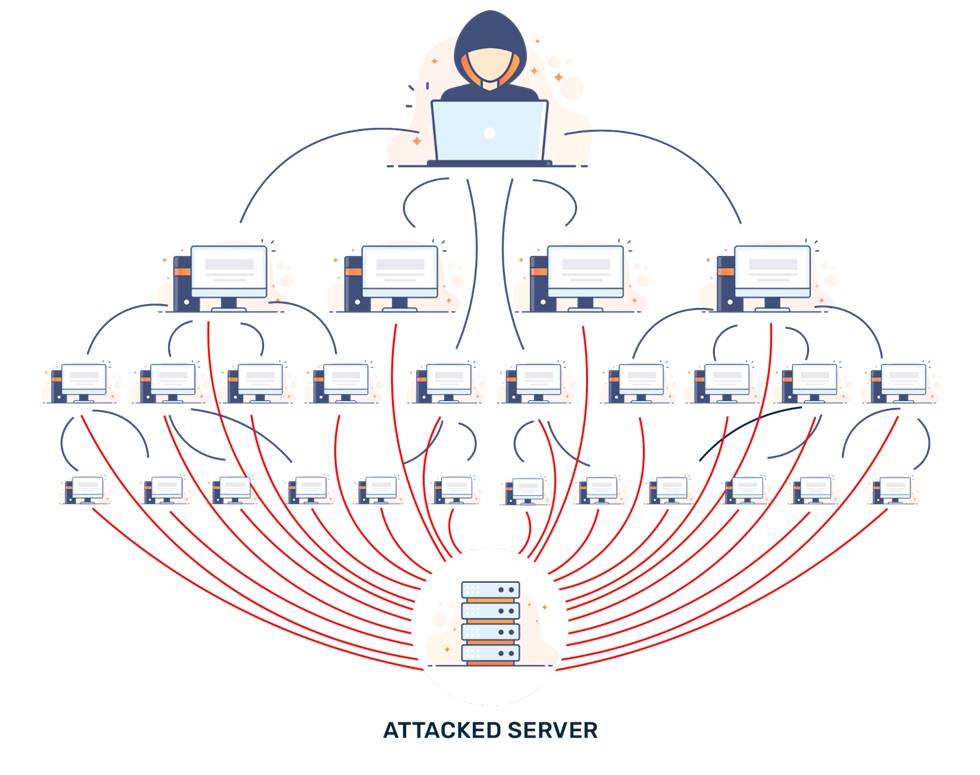
What are the Types of DDoS Attacks?
There are three major types of DDoS attacks: Application level attack, Volumetric attack, and Protocol attack. Let’s discuss them in detail and learn how to prevent them.
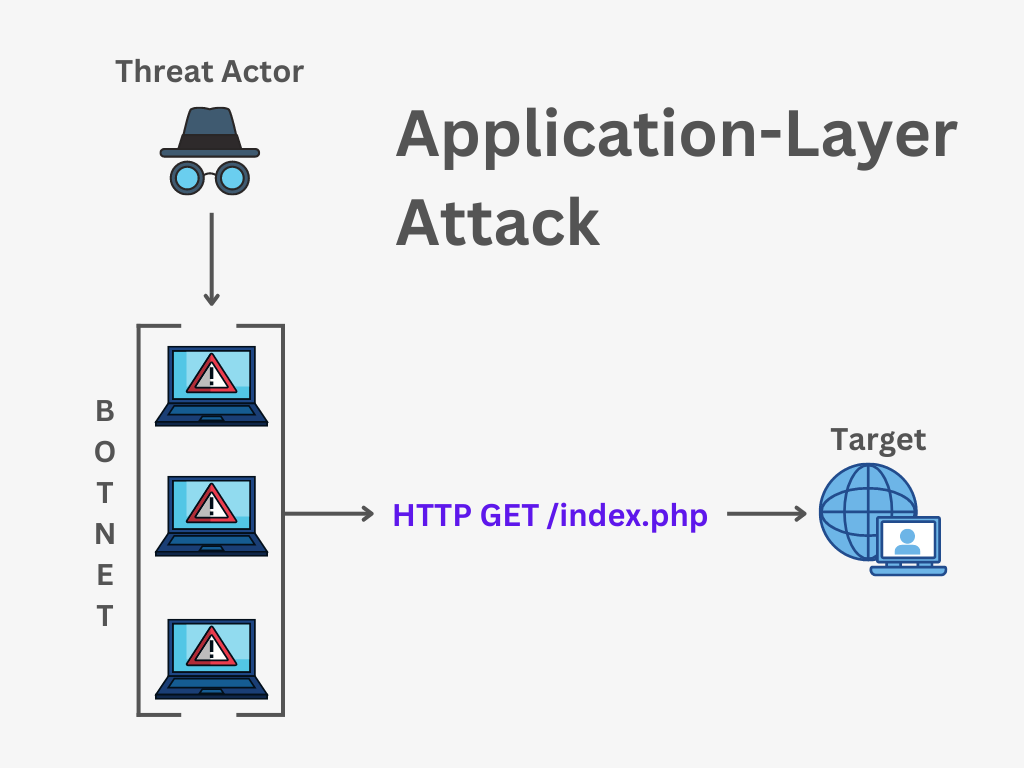
Application Attacks
An app layer DDoS attack, also called a 7 DDoS attack, disrupts an app’s content delivery by targeting its application issues. This type of cyber attack specifically targets the application layer. Its main goal is to cause disruptions in the delivery of content.
Source: https://blogs.blackberry.com/
These attacks target application layer protocols like HTTP and DNS, aiming to disrupt services or take control of application protocols. Application layer attacks are dangerous and sophisticated tools mostly used to attack user-facing applications and networks.
They can go undetected by traditional defense systems while still taking down websites or networks. Attackers target specific services or protocols with application layer attacks, making them a common way to disrupt services.
Examples of application layer DDoS attacks include HTTP GET/POST flood, Slowloris, and DNS amplification attacks. Companies invest in web application firewalls, threat mitigation solutions, and web traffic monitoring tools to stop application layer DDoS attacks.
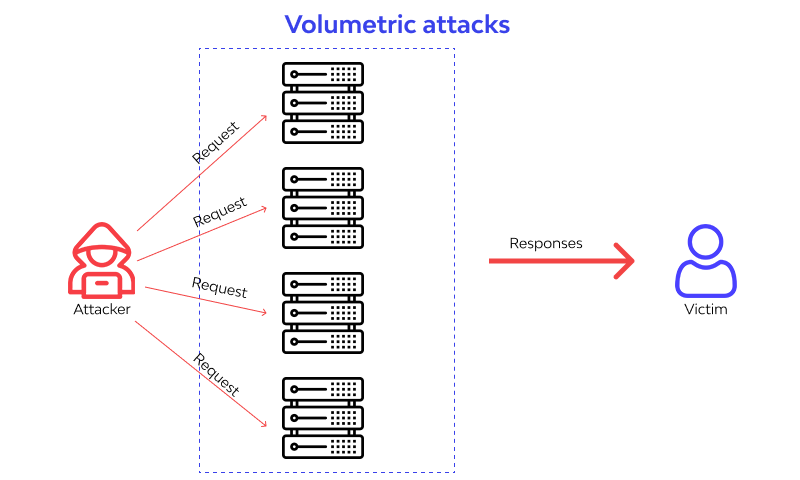
Volumetric Attacks
A volumetric DDoS attack overwhelms a network or server by flooding it with a large number of data packets. This is done to exhaust the available bandwidth. In these attacks, the target’s resources, such as bandwidth and processing power, are consumed, making it difficult for legitimate users to access the target’s resources.
Source: https://www.wallarm.com/
In most cases, volumetric attacks target critical SP services or enterprise customers. The target can be a specific network, server, or website. These attacks can involve sending a large number of data packets to the target, overwhelming its capacity to handle the incoming traffic.
The primary objective of a volumetric attack is to consume the available network bandwidth, making it difficult for legitimate traffic to pass through. It can result in extensive service disruptions and failures for users trying to access the targeted network or server.
Protocol Attacks
A DDoS protocol attack is a type of cyber attack that exploits weaknesses in network protocols to consume server resources and cause a denial of service. These attacks target the network layer protocols such as TCP, UDP, ICMP, and IP.
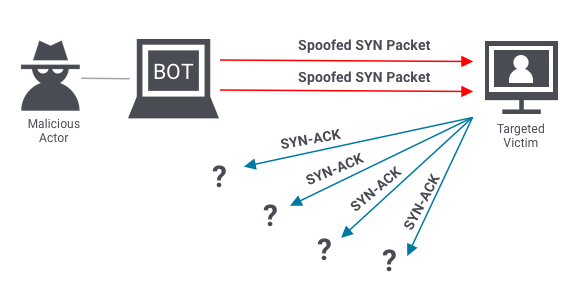
Source: https://www.onelogin.com/
Protocol attacks are designed to consume resources provided by the target, such as bandwidth and processing power, making it impossible for legitimate users to access them. This attack can have a significant impact by shutting down websites.
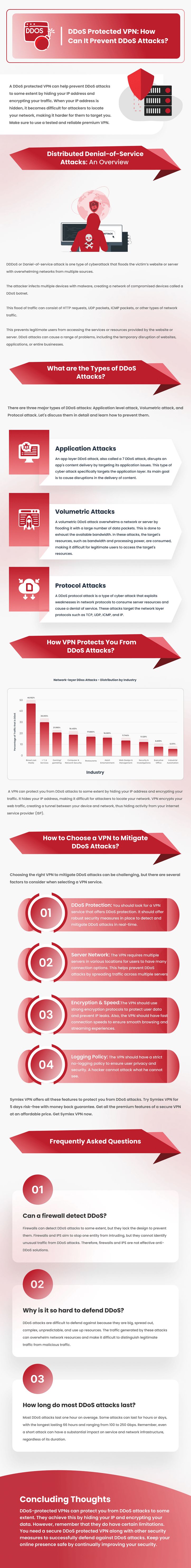
How to Choose a VPN to Mitigate DDoS Attacks?
Choosing the right VPN to mitigate DDoS attacks can be challenging, but there are several factors to consider when selecting a VPN service.
- DDoS Protection: You should look for a VPN service that offers DDoS protection. It should offer robust security measures in place to detect and mitigate DDoS attacks in real-time.
- Server Network: The VPN requires multiple servers in various locations for users to have many connection options. This helps prevent DDoS attacks by spreading traffic across multiple servers.
- Encryption & Speed: The VPN should use strong encryption protocols to protect user data and prevent IP leaks. Also, the VPN should have fast connection speeds to ensure smooth browsing and streaming experiences.
- Logging Policy: The VPN should have a strict no-logging policy to ensure user privacy and security. A hacker cannot attack what he cannot see.
Symlex VPN offers all these features to protect you from DDoS attacks. Try Symlex VPN for 5 days risk-free with money back guarantee. Get all the premium features of a secure VPN at an affordable price. Get Symlex VPN now.
Conclusion
DDoS-protected VPNs can protect you from DDoS attacks to some extent. They achieve this by hiding your IP and encrypting your data. However, remember that they do have certain limitations. You need a secure DDoS protected VPN along with other security measures to successfully defend against DDoS attacks. Keep your online presence safe by continually improving your security.
FAQs
Can a firewall detect DDoS?
Firewalls can detect DDoS attacks to some extent, but they lack the design to prevent them. Firewalls and IPS aim to stop one entity from intruding, but they cannot identify unusual traffic from DDoS attacks. Therefore, firewalls and IPS are not effective anti-DDoS solutions.
Why is it so hard to defend DDoS?
DDoS attacks are difficult to defend against because they are big, spread out, complex, unpredictable, and use up resources. The traffic generated by these attacks can overwhelm network resources and make it difficult to distinguish legitimate traffic from malicious traffic.
How long do most DDoS attacks last?
Most DDoS attacks last one hour on average. Some attacks can last for hours or days, with the longest lasting 66 hours and ranging from 100 to 250 Gbps. Remember, even a short attack can have a substantial impact on service and network infrastructure, regardless of its duration.
![Ultimate White Label VPN Business Guide 2026 [Cost & ROI]](https://symlexvpn.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/Ultimate-White-Label-VPN-Business-Guide-2025-Cost-ROI_2-376x114.webp)




